Gonads
The gonads, the primary reproductive organs, are the testes in the male and the ovaries in the female. These organs are responsible for producing the sperm and ova, but they also secrete hormones and are considered to be endocrine glands.
Testes
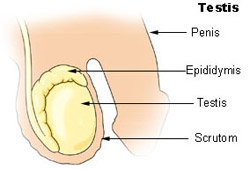
Male sex hormones, as a group, are called androgens. The principal androgen is testosterone, which is secreted by the testes. A small amount is also produced by the adrenal cortex. Production of testosterone begins during fetal development, continues for a short time after birth, nearly ceases during childhood, and then resumes at puberty. This steroid hormone is responsible for:
- The growth and development of the male reproductive structures
- Increased skeletal and muscular growth
- Enlargement of the larynx accompanied by voice changes
- Growth and distribution of body hair
- Increased male sexual drive
Testosterone secretion is regulated by a negative feedback system that involves releasing hormones from the hypothalamus and gonadotropins from the anterior pituitary.
Ovaries
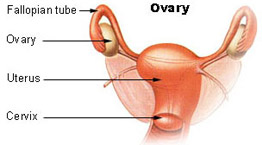
Two groups of female sex hormones are produced in the ovaries, the estrogens and progesterone. These steroid hormones contribute to the development and function of the female reproductive organs and sex characteristics. At the onset of puberty, estrogens promotes:
- The development of the breasts
- Distribution of fat evidenced in the hips, legs, and breast
- Maturation of reproductive organs such as the uterus and vagina
Progesterone causes the uterine lining to thicken in preparation for pregnancy. Together, progesterone and estrogens are responsible for the changes that occur in the uterus during the female menstrual cycle.
